选择排序(Selection Sort)
选择排序算法通过重复查找未排序部分的最小元素(考虑升序)并将其放在开头来排序数组。算法在给定数组中维护两个子数组。
- 已经排序好的子数组
- 剩下未排序的子数组
在选择排序的每一次迭代中,挑选未排序子数组中的最小元素(考虑升序),并将其移至排序后的子数组中。
1 | // Java program for implementation of Selection Sort |
时间复杂度:
冒泡排序(Bubble Sort)
冒泡排序通过反复交换相邻元素(如果顺序错误)来工作。
1 | // Java program for implementation of Bubble Sort |
优化实现: 即使数组已经有序,上述函数也会运行时间。如果内部循环没有引起任何交换,可以通过停止算法来优化它。
1 | // Optimized java implementation of Bubble sort |
时间复杂度:
插入排序(Insertion Sort)
1 | // Sort an arr[] of size n |
1 | // Java program for implementation of Insertion Sort |
时间复杂度:
链表的插入排序
1 | 1) Create an empty sorted (or result) list |
归并排序(Merge Sort)——分治思想
1 | MergeSort(arr[], l, r) |
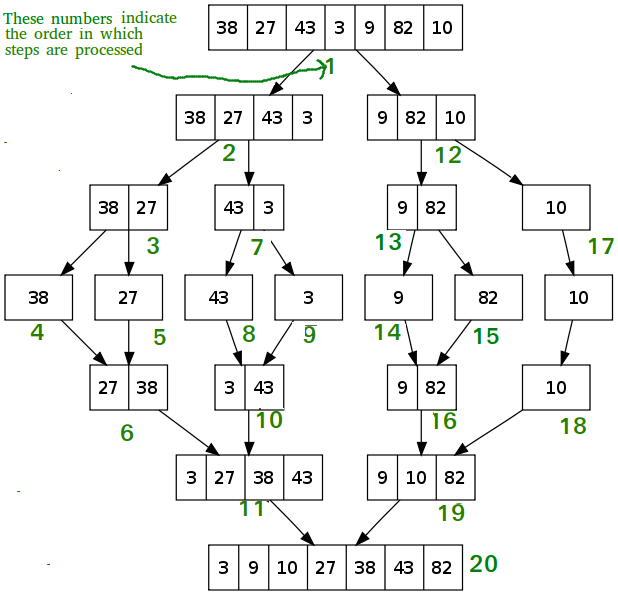
1 | /* Java program for Merge Sort */ |
时间复杂度:
链表的归并排序
1 | MergeSort(headRef) |
一下代码巧妙的使用两个指针移动来寻找中间节点,第一个指针每次移动一格,第二个指针每次移动两格,当第二个指针到达末尾时,第一个指针恰好到达中点。
1 | // Java program to illustrate merge sorted |
堆排序(Heap Sort)
堆排序是基于Binary Heap数据结构的基于比较的排序算法。它类似于我们首先找到最大元素然后和最后位置交换的选择排序。我们对剩下的元素重复相同的过程。
什么是Binary Heap
Binary Heap是一个完整二叉树,其中项以特殊顺序存储,使得父节点中的值比其两个子节点中的值更大(或更小)。前者称为最大堆,后者称为最小堆。堆可以用二叉树或数组表示。
用数组表示Binary Heap,如果父节点存储在索引i处,则左边的孩子索引为2 * i + 1,右边的孩子索引为2 * i + 2(假设索引从0开始)。
按升序排序的堆排序算法:
- 根据输入数据构建一个最大堆。
- 此时,最大的元素存储在堆的根。将它和堆的最后一项交换,然后将堆的大小减1。最后,heapify树的根。
- 在堆大小大于1的情况下重复上述步骤。
1 | // Java program for implementation of Heap Sort |
时间复杂度:
堆排序的应用
- 对几乎排好序的(或K个排好序的)数组进行排序。
- 求数组中的k个最大(或最小)元素。
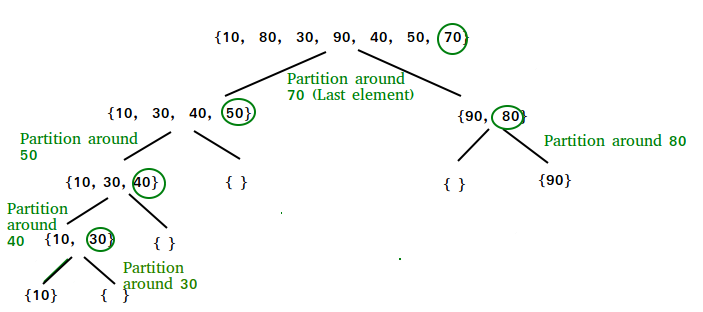
快速排序(QuickSort)——分治思想
快排选择一个元素作为枢轴(pivot),并将给定的数组根据选取的枢轴分区。有许多选择枢轴不同的方式。
- 始终选择第一个元素作为枢轴。
- 总是选择最后一个元素作为枢轴。
- 选择一个随机元素作为枢轴。
- 选择中位数为枢轴。
1 | public static void quickSort(int[] arr){ |
时间复杂度:
当最左元素或者最右元素被选为枢轴时,最坏情况发生在以下情形:
- 数组已经是相同的顺序。
- 数组已经是相反的顺序。
- 所有元素都相等。
所以尽量选择随机元素或者中间的元素或者中位数作为枢轴来避免最坏情况。
Shell Sort(希尔排序)
希尔排序基本思想为在直接插入排序的思想下设置一个最小增量dk,刚开始dk设置为n/2。进行插入排序,随后再让dk=dk/2,再进行插入排序,直到dk为1时完成最后一次插入排序,此时数组完成排序。
1 | public static void shell_sort(int array[],int lenth){ |
最坏时间复杂度为;最优时间复杂度为;平均时间复杂度为。辅助空间。稳定性:不稳定。希尔排序的时间复杂度与选取的增量有关,选取合适的增量可减少时间复杂度。

